Reviews by Team: Nonprofit Media
We look for quality sources of news and analysis in the public interest
In absolute numbers, no country holds more people in prison than the United States. The US also has the second highest incarceration rate – right after the Seychelles, an island archipelago with a population of 92,000 people. The racial disparity of the criminal justice system is well-documented. Combined with a constitution which permits forcing prisoners to work, and laws and practices which deprive felons of rights and opportunities even after release, America’s practice of mass incarceration has been linked to its history of slavery and racial segregation.
The issue is so severe that criminal justice reform has proponents across the political spectrum, but little progress has been made, even under the reform-friendly presidency of Barack Obama (the first sitting president to visit a federal prison).
One man who has made the cause his own is Neil Barsky, formerly the manager of a hedge fund named Alson Capital Partners, which managed $3.5B of capital at its peak. In 2014, Barsky launched The Marshall Project, named after Thurgood Marshall, the first African-American Supreme Court justice and a towering figure in US civil rights history. The name might suggest an advocacy organization, but The Marshall Project is a nonpartisan, nonprofit journalism venture.
Barsky himself pursued a career in journalism before he went into finance, and he brought on board Bill Keller as editor-in-chief, further boosting the project’s journalistic credentials.
Keller was the executive editor of the New York Times from 2003 to 2011. His long tenure there was not without its controversies. For example, he was a “reluctant hawk” arguing in favor of the Iraq war, something he later half-apologized for, only to argue in 2013 that the US should “get over Iraq”, arm more Syrian insurgents, and force Syria’s ruler Assad out of power.
Be that as it may, Keller/Barsky quickly turned The Marshall Project into a sizable journalistic venture and a professionally run nonprofit organization exclusively focused on the cause of criminal justice.
Stories are published through its own website, and sometimes in partnership with other media organizations, both for-profit and nonprofit. Together with ProPublica, the project won a Pulitzer Prize for “An Unbelievable Story of Rape”. It’s a harrowing tale of how police pressured a woman to recant a report of a brutal rape, instead of tracking down her attacker, who would go on to commit five other attacks.
Funding, Transparency, Executive Compensation
The project is funded partially by Barsky himself, but it has also received funding from foundations and major donors, including some of the usual funders such as Ford, MacArthur and Rockefeller. Its 2015 Annual Report provides a high-level breakdown of funding sources: 55% foundations, 43% individual donors. According to its latest financial statements, revenue for 2015 was about $4.8M.
The Annual Report also gives a sense of how the organization views its own impact, recapping its important stories of the year, and sometimes drawing a connection between investigations and real-world impact, for example:
After we published Attica’s Ghosts on brutality at New York’s infamous upstate prison, the Department of Justice launched an investigation, cameras were installed inside the stairwells, and the three guards finally pleaded guilty.
This impact assessment is not as systematic yet as the ones performed by some other organizations, but it is only the organization’s first Annual Report.
The latest available tax return reports that Keller received total compensation of $225K in 2014, though his annual compensation may be higher given that he still worked at the NYT in early March of that year. Regardless, it is well below some of excessive nonprofit compensation we’ve written about, e.g., the $584K Paul Steiger received in his first year at ProPublica.
Positioning
The Marshall Project defines its mission as “creating and sustaining a sense of national urgency about the U.S. criminal justice system”. I appreciated the clarity of the letter from the founder and the letter from the editor in setting out the organization’s agenda. Barsky writes in his letter, about the criminal justice system:
What struck me was not only how expensive, ineffective, and racially biased it is, and how difficult it is to find anyone, liberal or conservative, who defends the status quo. But also how our condition has become taken for granted.
He argues that the truth speaks for itself:
We do not need to be strident or ideological or selective in our use of facts. When the truth is as disturbing as it was in the segregated South, or in Vietnam, or today’s prisons and courts, truthful reporting can have a powerful impact. We will explore what is working as well as what is broken, and where the potential exists for meaningful reform.
He concludes:
Being nonpartisan is not the same as being neutral. We approach the issue with the view — shared by a growing number of conservatives and liberals — that our system needs serious rethinking.
For his part, Keller promises in his letter that “you will find here the voices of progressives and conservatives, centrists and provocateurs”.
Content Formats
Most of the content is long-form text, with a few interactives, and a limited amount of data journalism. As noted above, many stories are partnerships with other news organizations. This means they are also often published in traditional publications like The New York Times, or broadcast in other formats such as audio versions for NPR.
There is a small YouTube channel used to host videos that accompany some stories, and it does not have a large audience in its own right (548 subscribers as of this writing).
I find the focus on long-form journalism refreshing compared with other media that attempt to do a little bit of everything (podcasts, videos, etc.). That said, compared with sites like Vox, The Marshall Project still has some ways to go in making complex topics accessible, especially when it comes to data journalism.
Content Example: “Opening statement” Newsletter
On most pages, The Marshall Project encourages readers to subscribe to its newsletter, “Opening Statement”. It’s a roundup of criminal justice news that includes original reporting, but isn’t limited to it. I must say, it is very well curated. For example, the first item in today’s newsletter is this:
“My intuition tells me that if I go in, I’m not coming out.” Jeanette Vizguerra, an immigrant mother of three American children, is taking refuge in a church in Colorado rather than report as ordered for another meeting with federal immigration officials. She was ordered deported under the Obama administration after a conviction for using false ID, but was granted repeated postponements. She’s given her kids instructions about what to do if and when the feds come. THE NEW YORK TIMES Related: Feds defend arrest of first “dreamer;” say he’s a gang member. DHS More: Now ICE is detaining victims of domestic abuse, evidently on tips from their alleged abusers. EL PASO TIMES
Highlighting these particular news items, including in the email subject (“A mother claims sanctuary”), demonstrates excellent editorial judgment. These incidents help explain why many communities have chosen to protect undocumented individuals by declaring themselves “sanctuary cities”. At the same time, it is laudable to see a direct link to the DHS statement, even if it may undermine a strictly activist narrative.
While there is some room for improvement (headlines like “N/S/E/W” or “ETC.” are not especially helpful), the newsletter is definitely one that I’ll stay subscribed to. I especially appreciate that it does not give Marshall Project content special placement, but just attempts to highlight the most important stories of the day, wherever the may be found.
You can view past issues of the newsletter before subscribing.
Content Example: “The Deadly Consequences of Solitary With a Cellmate”
This story, which came out in March 2016, highlights the issue of prisons putting more than one inmate in cells designed for solitary confinement. According to the story, “at least 18 states double-up a portion of their restrictive housing, and over 80 percent of the 10,747 federal prisoners in solitary have a cellmate.” A primary reason for this practice is prison overcrowding.
The story shows what anyone might expect: that sometimes, inmates attack or even kill each other under such circumstances. A chilling quote from the story:
After two months of begging for a single cell, Fox wrote a note to guards: “Move my cellie or I’m going to erase him.” They didn’t, so he did.
The Eight Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits cruel and unusual punishment, but in a historically very punitive society, this is a high bar to meet in court. Reporting like The Marshall Project’s is essential to expose prison practices that amount to extrajudicial death sentences for inmates.
The story is well-written, uses neutral language, refers to many primary source documents, and makes good use of photographs, drawings, and an interactive 3D illustration. It was done in partnership with NPR.
Content Example: “Everything You Think You Know About Mass Incarceration Is Wrong”
On the occasion of his book release, the project is giving exposure to John Pfaff’s work, which questions the common narrative that the “war on drugs” is the key driver of mass incarceration.
While I have no reason to question the integrity of Pfaff’s work, as presented here, it neglects the well-established link between drug criminalization and organized crime: drug money fuels other criminal activity and sustains criminal gangs and organizations. The story also does not touch on the effect drug-related felony convictions may have on people’s lives. In this way, the “war on drugs” can be empirically argued to have ripple effects far beyond its directly measurable effect on the prison population.
In fairness, the authors reached out to Michelle Alexander (The New Jim Crow) for a quote regarding Pfaff’s work, and she speaks to some of the drug war’s other ripple effects. Moreover, presenting provocative theses like Pfaff’s is certainly consistent with The Marshall Project’s mission, and it usefully expands our understanding of the big picture. Still, I would have preferred a less sensationalist headline and a more balanced approach.
Design, Tech and Licensing
The Marshall Project website is easy to navigate and mobile-friendly. It employs a tagging system it calls The Record to organize stories about subjects like immigration or prison life. One very neat feature of this taxonomy is that it’s used both for The Marshall Project’s own stories, and for stories from around the web.
There is no comment section or discussion forum, and content is under conventional copyright, though there is no copyright notice.
The site’s jargon, design and iconography are a bit idiosyncratic (i.e. you have to poke around a bit to figure out how the site is organized, rather than being able to apply a mental model from other sites). This reflects the use of a custom software developed for the project and recently published on GitHub under the MIT License with an explicit warning that “we cannot support any use of this code, in part or in whole.”
Beyond its content management system, The Marshall Project has a very active GitHub presence. Unlike the CMS, the project’s news monitoring tool, Klaxon, is designed for use by other journalists and has been forked by other organizations, e.g., by the Associated Press.
This is a big deal – if news organizations, thanks to leadership by nonprofits, can open up their technology layer, it will improve journalism for everyone.
The Verdict
The Marshall Project tackles a systemic issue that affects millions of lives in the United States – criminal justice – and it does so without deviating from the simple premise that shedding the light of quality journalism on the issue can lead to positive change.
Having only been around for a short time, the project has already demonstrated the value of this proposition. The collaboration with other media, and the use of open source tools, expand its impact beyond the website and newsletters. The team’s curatorial work in monitoring news from around the web is excellent.
The project’s nonpartisan outlook may predispose it slightly towards ideas and voices that appeal to centrists. Sex workers pushing for legalization, for example, may be frustrated to see only a single article on the subject: an interview with an advocate for strict application of the Nordic model (prosecuting johns but not prostitutes). This in spite of the fact that major organizations like Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch advocate for full decriminalization of “sex work that does not involve coercion, exploitation or abuse” (Amnesty).
Systemic issues like sex work and drugs benefit from systematic explanations, e.g., backgrounders and data briefs. ProPublica ended up building an entire section for data journalism; Vox is well-known for its slightly clickbaity but useful “Gun violence in America, explained in 17 maps and charts” type articles. There may be opportunities for collaboration both with journalistic organizations and with think tanks and NGOs.
Still, these criticisms are not serious enough to subtract points from the final rating: 5 out of 5 stars. The Marshall Project is already very good at what it does, and I highly recommend following their work. You can follow them on Twitter, on Facebook, and via the Twitter list of all media rated 4 stars or higher.
“Filter bubbles” of news consumption reflect divergent values. If you believe that abortion is murder, the fact that major US media are not continually reporting on the issue, and on the efforts by fellow activists, must seem like a grave injustice. Personally, I don’t believe that abortion is murder, so I can’t agree with that concern.
Carl Sagan and Ann Druyan have given one of the best explanations I’ve ever found, looking at fetal brain activity as the chief characteristic that defines being human. Because, like them, I don’t recognize the claim to personhood in the early trimesters of pregnancy as even based in any kind of scientific reality, the grave consequences of denying women the right to make this decision on their own are the actual injustice deserving attention in my view:
- the fundamental violation of body autonomy that any state intervention represents;
- the association of the “pro-life” movement with terrorism against abortion clinics and doctors and intimidation/harassment of women
- the intended and unintended side effects of anti-abortion efforts on family planning and women’s health services well beyond abortion (e.g., contraceptive services, STD diagnosis and prevention, etc.);
- the increases in unwanted pregnancies (which in turn may lead to adverse outcomes for children and parents) and unsafe “back alley abortions”.
From that point of view, major media in the United States are not paying sufficient attention to the unholy matrimony between the Republican Party and “pro-life” groups (including associations with religious extremists who have endorsed anti-abortion violence). To the extent that media do report about the issue, it is usually about the work of politicians, not the real-world impact of their policy decisions. This creates a distorted picture.
If you share this perspective, then Rewire may be a welcome addition to your nonprofit news mix. Recently rebranded, it has been around since 2006, originally under the name “RH Reality Check” (archived contents). It reports chiefly on reproductive rights issues. With an ethos of intersectionality, Rewire does give some attention to issues such as LGBT rights, race and immigration, and economic justice.
Transparency and Compensation
RH Reality Check was part of the UN Foundation from 2006 to 2012. This may not be surprising once you realize that the UN Foundation (which is independent of the UN and supports its work) was CNN founder Ted Turner’s billion-dollar gift to the world. Turner is a long-time reproductive rights and population control advocate.
Rewire has since left the UN Foundation mothership and is now an independent nonprofit (tax returns). Like other nonprofit media, it is largely dependent on grants from foundations, which nowadays includes funders like the Packard Foundation, the Compton Foundation and the Ford Foundation [CSV file].
The Rewire website does not mention these sources of funding or provide a breakdown, and Rewire did not respond to repeated inquiries about funding and other matters. The tax returns do show a large increase in revenue from $1.18M (2013) to $5.95M (2014). At $181K, the compensation of President/Editor-in-Chief Jodi Jacobson is not unusual for a nonprofit of this size.
There is no Annual Report or other statement of impact, and as such, it’s difficult to assess to what extent stories broken by Rewire have impacted real-world policy decisions or activist efforts.
Positioning
While stating its pro-choice positioning clearly, Rewire also identifies with the Code of Ethics of the Society of Professional Journalists. Commentary and news content are distinguished, though news stories don’t shy away from value judgments. This, for example, is from a news story about Donald Trump’s appointment of Jeff Sessions as Attorney General:
Senate Judiciary Committee Republicans in Sessions’ confirmation hearings largely dismissed his abysmal record on a broad range of rights—including, but not limited to, voting, reproductive, and LGBTQ rights, all of which are intertwined. [Emphasis mine]
Politically, Rewire is most closely identified with feminism. In 2016, it published a column expressing concern about harassment of Bernie Sanders’ critics by online trolls (adopting the “Bernie Bro” term and drawing parallels to Gamergate), but far from being a pro-Clinton piece, the article is a pretty nuanced feminist take on the subject. Later in the campaign cycle, editor Jodi Jacobson expressed frustration with the possibility of a Vice President Tim Kaine given his poor track record on abortion.
Content Example: “False Witnesses”
Rewire’s primary focus is in-depth reporting on abortion, contraception, and women’s health. A section called False Witnesses highlights “pro-life” activists who are sometimes cited as experts, but who (according to Rewire) are promoting false information.
To take a closer look at an example chosen at random, Rewire calls Chilean researcher Elard S. Koch a false witness for his efforts to discredit the well-established link between anti-abortion laws and unsafe abortions which put women’s health at risk.
After being rejected without review by The Lancet, Koch published his study in PLoS ONE, a journal known for publishing, then retracting a paper referring to the human hand’s “proper design by the Creator”. (PLoS ONE uses an expedited review process which does not examine a paper’s importance.)
After taking a look at the Koch paper, the Rewire analysis, the Guttmacher Institute assessment, and the Koch reply, I agree that the Koch paper draws unwarranted conclusions from the actual findings.
To make a long story short, the combination of rising incomes / improving education, legal access to family planning (including contraceptives) and illegal access to abortion-inducing drugs have helped bring abortion-related maternal deaths in Chile down, in an environment that has never been very tolerant of abortion. The remaining extent of maternal deaths resulting from unsafe abortion procedures is unknown, because they are by definition part of a clandestine crime under Chilean law.
The Koch paper doesn’t refute the well-established fact that countries which experience large numbers of maternal deaths caused by unsafe abortions could reduce those deaths by legalizing abortions. Its findings only suggest that the long process of reducing unwanted pregnancies through family planning/contraceptives, rising incomes, improving education, etc. can also contribute to doing so.
As a “pro-life” researcher, Koch overstates what can be learned from the data, and those who use it for their purposes likely overstate it further. Nonetheless, I did not find the Rewire piece especially helpful in piecing this together. For example, Rewire doesn’t mention legal access to contraception and doesn’t talk about illegal access to abortifacient drugs like misoprostol, both of which are important factors in maternal mortality. Its essay reads like a he-said/she-said that doesn’t quite warrant the classification of Koch as a “false witness”.
Indeed, unlike a fact-check scale like Politifact or Snopes, a classification system that personalizes ratings by labeling individuals “false witnesses” is strongly predisposed towards a one-sided portrayal. This is perhaps understandable given that both sides in the abortion debate are “fighting for human lives” from their respective vantage points, but it’s an example of a slightly sensationalist bent that may not serve the most truthful journalism possible.
Content Example: “Fake Abortion Clinic” Investigation
Rewire also does in-depth investigative journalism in a dedicated section. A recent investigation, “A Window Into Texas’ Publicly Funded Fake Abortion Clinics”, is a good example. It is based on public records requests regarding Texas’ “Alternatives to Abortion” program and makes the case (with input from health experts) that this program leads to women being preyed upon by organizations that promise health services, but that are primarily on a mission to minimize abortions rather than providing care.
Given its pro-choice premise and use of loaded language like “fake clinic” and “anti-choice propaganda”, Rewire’s investigation is unlikely to reach the large number of Americans who support access to contraceptive services but not abortion, and who might be shocked by the taxpayer-funded proliferation of “women’s centers” that don’t provide much more than an ultrasound and a prayer. Leaving this aside, the story is an example of quality investigative work that sheds light on the consequences of Republican health policies.
Design and Licensing
When it relaunched as Rewire, the site shed a dated look in favor of a clean, pleasant and mobile-friendly design. Color and layout are used effectively to meaningfully divide content by topics and content types (e.g., news vs. commentary). As with many good designs, there are multiple ways to go to the same place, aiding discoverability of the site’s content and structure.
A lot of content is loaded on-demand, which causes problems reaching links at the end of the page, since new content may be loaded before you can click on a footer link (a familiar problem with the “infinite scroll” design pattern). The on-demand loading of content doesn’t work when JavaScript is disabled, rendering the site partially unusable without JavaScript. There is no commenting system of any kind.
The site prominently advertises an email newsletter called Rewire daily. Each email contains headlines and summaries of stories, linking back to the main Rewire site. The email database is likely also used for fundraising appeals, though I have not received one yet.
Content is under conventional copyright, i.e. it may not be copied or re-used without permission.
The Verdict
Rewire is without a doubt a useful resource for anyone concerned about reproductive rights in the United States, an issue which is especially relevant given the onslaught of legislative attacks in many US states and the hostile environment for women’s rights under the Trump administration.
As a news site, its commitment to intersectionality is reflected in its selection of stories, e.g., an in-depth investigation of reproductive rights may be posted alongside an update on the Dakota Access Pipeline. The underlying assumption – that different movements’ struggles deeply relate to each other – may benefit from more explicit explanatory context in some cases.
I was disappointed by the lack of organizational transparency (no reporting on impact, no financial breakdown, only a “we will get back to you” response to an email inquiry without any further follow-up) and with a slight tendency towards sensationalizing in service of its agenda.
Because of these concerns, I subtract 1.5 points off its rating per the review criteria. This results in a rating of 3.5 out of 5 stars, rounded up to 4 given that Rewire fills a niche of specialized journalism that is not currently occupied by other nonprofit news sources. As such, Rewire is now also part of the Twitter list of quality nonprofit media.
(March 13, 2017: re-worded paragraph in conclusion that relates to intersectional coverage)
(March 16, 2017: removed paragraph that referenced the #NoBanNoWall tag below the site’s logo; Editor-in-Chief Jodi Jacobson clarified that it was a temporary placement as part of highlighting trending topics below the logo)
What is integrity? We expect governments to act in the public interest, to root out corruption, to uphold the rule of law. We expect businesses to follow the law, to pay their fair share of taxes, to not abuse their power. We expect nonprofits to act in accordance with their mission, to avoid wastefulness, to be transparent.
The Center for Public Integrity (CPI) is an investigative journalism nonprofit based in Washington, D.C. that’s dedicated to documenting abuses of power in these and other institutions. It defines itself as nonpartisan and has indeed conducted many investigations across the political spectrum.
Although its name and location might suggest a “think tank” type organization, CPI is fully focused on producing journalism – often published in partnership with other news outlets.
Funding and Executive Compensation
Founded in 1989, CPI had revenue of about $9M in 2015. According to its Annual Report, almost all of its revenue comes from grants and donations. Most of its support comes from large gifts and grants (many from the typical foundations that fund journalistic work); in 2016, CPI received $210K in donations smaller than $250.
As of November 2016, CPI’s CEO is John Dunbar, an investigative journalist and CPI veteran. Because of the recency of his appointment, compensation information is not available yet; his predecessor received $301K from the Center in 2015, which is squarely in the middle between ProPublica and the Center for Investigative Reporting in terms of executive compensation.
CPI states: “We maintain a strict firewall between funding and our editorial content.” It publishes its editorial standards which include a requirement for full disclosure of conflicts of interest, and a commitment to avoid such conflicts where possible.
Reporting
Compared with ProPublica and CIR, CPI has a stronger focus on institutions, both public and private. With regard to government, since 2001, no news organization other than the New York Times has filed more Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) lawsuits than CPI, according to a report by the FOIA project. These types of lawsuits are necessary to challenge government over-classification of materials.
The recent CPI report regarding what amounts to a massive gift to the insurance industry by the taxpayer-funded Medicare program is an example of an investigation that was made possible through a FOIA lawsuit.
CPI investigates both Republicans and Democrats, and I was not able to detect a bias towards either group. The report on ambassador postings for donors to the Obama campaign is a good example of data-driven journalism targeting the Obama administration, while CPI also reported in detail on the perks and access offered to big donors to Donald Trump’s inauguration.
Businesses are far from immune from CPI’s investigations. In 2014, CPI received a Pulitzer prize for an investigation which revealed “how doctors and lawyers working at the behest of the coal industry helped defeat benefit claims of coal miners who were sick and dying of black lung disease.”
After the 2008 financial crisis, CPI published some of the most in-depth reporting on the links between banks that received bailout money and the subprime lenders that caused the crisis. Through the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, which it launched in 1997 and which it houses, CPI has helped bring about the most important investigations into tax havens and offshore banking in recent history, including the Panama Papers investigation.
CPI publishes a running log of all corrections.
Website, Licensing
CPI’s website is easy to read and offers section views for its primary ongoing investigative domains (e.g., politics, business, environment). The content is not sensationalized, and as with other investigative sites, you’re probably more likely to read an investigation of interest to you through a social media or RSS feed than by going directly to the site. Content is generally in text form, and the site looks reasonable on mobile devices.
Donation appeals are visible but not annoying. Stories use Facebook comments as a discussion system; commenting guidelines are buried in the terms of use, and I did not see evidence of moderation (which doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen). Content is under conventional copyright and sometimes cross-published to other news media. In general, CPI is a cathedral-style journalistic organization with limited community engagement.
The Verdict
I would recommend CPI without reservations for your RSS or social media feed. The institutional focus distinguishes it from ProPublica and CIR, and this focus has led it to dig into some of the largest scale, most systemic abuses in areas such as the financial services industry. Its incubation of the International Committee for Investigative Journalists was a brilliant move in that regard, since many of the most complex tax avoidance schemes are international in nature. This makes CPI/ICIJ truly indispensable.
It’s not surprising that an organization with “Integrity” in the name does a good job with organizational transparency. Financial documents and annual reports are easy to find, and the donor information is comprehensive. In spite of all these editorial and operational strengths, CPI still has a relatively small online presence – 74K followers on Twitter, 83K on Facebook.
Doing more to engage (and involve!) readers through these channels without compromising on its strengths may help build a larger audience, which in turn may translate to more bottom-up funding. Given that CPI, ProPublica and CIR are all nonpartisan, we might also hope for more collaboration between them in future.
Because of its high impact business and government investigations, I give CPI 4.5 out of 5 stars, rounded up. It is now also in the Twitter list of quality nonprofit media.
In 1977, long before the Internet gave new life to nonprofit media, Bay Area journalists David Weir, Dan Noyes, and Lowell Bergman founded the Center for Investigative Reporting (CIR) in Oakland, CA. The nonprofit organization’s mission is to create investigative journalism that “sparks action, improve lives and protects our democracy”.
It did so initially by working primarily with other news outlets. A first major collaboration was a 1978 exposé by Kate Coleman and Paul Avery regarding the Black Panther Party and its involvement in organized crime, including murder. Since then, CIR has produced deep investigations about all sectors of society, for example:
-
“Reasonable Doubt” (with CNN), a 2007 investigation into poor quality controls at forensic crime labs
-
“Dirty Business”, a 2009 documentary about the myth of clean coal
-
“The God Loophole”, a 2016 investigation of abuse at religious daycare facilities
CIR has received numerous journalism awards, including a Peabody, and the organization was a finalist for a Pulitzer prize in 2012 for its investigation of earthquake safety of California schools.
This focus on wrongdoing in any part of society makes it similar to the younger, NYC-based ProPublica, and indeed, in many ways, CIR is its West Coast counterpart. The two organizations had nearly the exact same amount of revenue in 2014 ($10,324,242 vs. $10,324,275) and draw funding from similar sources, primarily foundations and major gifts.
Unlike ProPublica, CIR does not provide a breakdown of its revenue by source, but it does provide a list of supporters, which includes Gates, Carnegie, Rockefeller, Open Society Foundations, Hewlett, MacArthur, Knight, and many of the other big names in philanthropy. An editorial independence policy is meant to make it clear that such support does not influence reporting.
One notable difference between the two is executive compensation. CIR pays its Executive Director a total of $232K, while ProPublica’s highest compensated “co-executive” makes $429K. CIR does not publish an Annual Report, but it does use an open source impact measuring tool to produce whitepapers documenting the real world effects of some of its most notable investigations.
As an older organization, CIR had to transform itself for the Internet. It now publishes its investigations on Reveal, which features in-depth reporting, podcast episodes, videos, and occasional data journalism. The grouping of investigations (e.g., “Hidden abuses under the watchtower” for its Jehovah’s Witnesses investigation) makes the current focus areas reasonably clear.
While it utilizes text, audio and video for its reporting, in many other respects, Reveal is very old school. There is no commenting system, content is under conventional copyright (as opposed to a Creative Commons License), and the heading “Get involved” only leads to an ask for donations.
The Verdict
As with ProPublica, the universal search for abuse (and the heavy reliance on conventional funding) can make it harder to address system-level issues such as inequality, climate change, electoral injustice, or mass incarceration. Efforts like CIR’s are therefore no substitute for values-driven journalism that provides consistent emphasis on systemic injustice.
On the other hand, the Center’s investigations into all sectors of society do help people to learn about (and act on) abuse and wrongdoing within their communities. On that basis, I recommend following Reveal, and the feed is now part of the Twitter list of quality nonprofit media. 4 out of 5 stars.

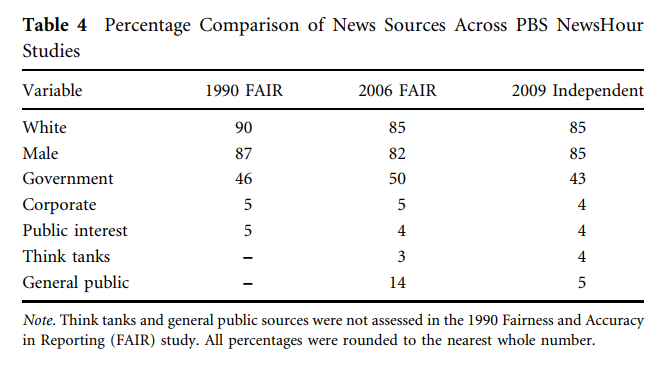
Journalists like David Brooks and Mark Shields provide background on the news, reflecting a general bias of sourcing (85% male, 85% white) that has been consistently documented.
NewsHour is the flagship public television news program in the United States, distributed by PBS and produced as a collaboration between key member stations. As with all public broadcasting in the US, it relies on a mix of funding that includes government support, corporate underwriting, foundations, major donors, and small donors. PBS programs are subject to funding standards, and an ombudsman serves as a verbose internal critic.
Executive compensation at some member stations reaches excessive levels by nonprofit standards – nearly $600K for WNET CEO Neal Shapiro (WNET co-produces NewsHour). This is a reflection of competition for talent with for-profit media (Shapiro was previously the President of NBC) and the large organizational size, but still merits scrutiny as it can reinforce leadership trading within a media oligopoly as opposed to the development of a unique nonprofit media leadership path.
NewsHour made its debut as a nightly news program in 1983. It features headlines, interviews, and some in-depth reporting. Episodes can be streamed online, and segments of the program are routinely transcribed. Probably the biggest difference with for-profit news programs is tone, not content. The program projects a sense of respectful, calm, civil engagement with the issues of the day. That’s no small thing in an era where networks like CNN employ extreme partisans just to shout at each other. Of course, it can also contribute to normalization of extremes.
As far as content is concerned, NewsHour does generally take a longer, more global view than many other news programs. It routinely features topics from US history, developments in other cultures, and so on. The commitment to balance that’s part of the public broadcasting mandate typically translates to having a center-left and a center-right guest on the show for purposes of analysis (such as the Brooks and Corn / Shields and Brooks programs).
Studies both by progressive media criticism organization FAIR and by independent researchers have consistently shown that the sources NewsHour consults for expertise and interviews are 85% male, 85% white (the US is about 72% white), and about 45% government. Public interest sources, think tanks, and corporate sources are each sourced about 4-5% of the time.
That means organizations that are deeply familiar with topics like the drug war, voter suppression, the arms trade, etc., are rarely put on the air to talk about them. In its selection of core stories of the day, NewsHour also largely mirrors the choices of other news programs. There are exceptions, such its recent in-depth feature on the under-reported United States prison strikes, which is also notable in being singular.
The program exists in the larger context of public broadcasting in the US, which is frequently the target of efforts to either politicize or defund it. While government funding has its perils, the reliance on major donors and corporate underwriters also comes at a cost. Most significantly, Jane Meyer of the New Yorker exposed in 2013 how PBS member stations got cold feet about programs putting the spotlight on a major donor and trustee, David Koch of the infamous Koch Brothers.
Given this combined political and corporate influence, a program like NewsHour is likely to stay firmly within the Overton window in its reporting: views that are “too radical” either on the left or on the right will rarely be aired. But of course the window isn’t fixed – it remains to be seen how NewsHour will deal with the normalization of hate, and with politics under President Donald Trump.
The Verdict
For the time being, I still recommend NewsHour with reservations, since it at least leans towards public interest reporting rather than pure ratings-driven entertainment. It is a good bellwether of elite opinion, and provides more nuanced and careful analysis than any other centrist US news program I’ve seen.
3.5 out of 5 stars, rounded up. If you follow our Twitter list of quality nonprofit media, you will get updates from NewsHour alongside more political and adversarial sources like Mother Jones, The Intercept, and Democracy Now!, as well as the academic perspectives from The Conversation.
“The world deserves access to its greatest minds”, the slideshow begins, showing images of war zones. “Now more than ever the world needs access to reliable information.” The video is a fundraising ad for Project Syndicate, a nonprofit based in the Czech Republic.
The location reflects the organization’s original purpose. Project Syndicate was started in 1995 to help syndicate the views from “leaders and thinkers” from Western and Western-aligned countries to Eastern European newspapers. Today, it explains its model as follows:
News organizations in developed countries provide financial contributions for the rights to Project Syndicate commentaries, which enables us to offer these rights for free, or at subsidized rates, to newspapers and other media in the developing world.
While its tax returns are not publicly viewable, Project Syndicate’s CEO assured me that “it is registered as a public benefit corporation, 501c3 equivalent, in the Czech Republic. As such we register audited financials, board minutes, annual reports, etc every year with the appropriate Czech courts as required by Czech law.” He broke down the revenue composition of the organization as 60% subscriptions, 37% foundations, and 3% donations.
The website lists the Gates Foundation, the European Climate Foundation, and the UAE-based Al Maktoum Foundation as funders. That list is incomplete and may only reflect recent funding; George Soros’ Open Society Foundations, for example, gave $350,000 in 2014.
PS columns are translated by PS into multiple languages, and into many more by the participating newspapers. Each column includes a small speaker bio, but not a disclosure statement like the ones found in The Conversation (which I reviewed here).
Indeed, even funders themselves use PS to get their views out to newspapers around the world. This includes many columns by George Soros and by Bill Gates, two by Melinda Gates, and four by Mohammed bin Rashid al Maktoum. Each story includes an author bio, but does not disclose these funding connections.
Beyond its funders, the “greatest minds” whose opinions Project Syndicate spreads around the world include former and current world leaders, experts in academia, Nobel Prize Winners, and for whatever reason, Bjørn Lomborg. Lomborg, whose Ph.D. is in political science, has turned being a contrarian on environmental issues into a career, and his policy work (which many experts have described as scientifically dishonest) tends to be used by conservatives to justify luke-warmism: watered down approaches to solving environmental issues.
Columnists from politics include former UK Prime Ministers Gordon Brown and Tony Blair, former UN Secretary General Kofi Annan, former German foreign minister Joschka Fischer, and former US national security advisor Zbigniew Brzezinski.
Some of these folks are life-long public servants, others (like Blair and Fischer) have turned their post-politics careers towards more lucrative objectives. Blair in particular has been busy: consulting for the financial services industry, advising dictators through Tony Blair Associates, making a secret deal with a South Korean oil firm. None of these connections are disclosed in his PS bio, which focuses solely on Blair’s work through NGOs and academia:
Tony Blair was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007. Since leaving office, he has founded the Africa Governance Initiative, the Tony Blair Faith Foundation, and the Faith and Globalization Initiative.
This shows why disclosure statements are important.
By uncritically publishing views by Blair, Gates, Fischer, Brzezinski and other members of political and economic elites, PS implicitly will be less likely to air voices that are highly critical of them. This is not a publication that will give much credence to voices that allege that Henry Kissinger was a war criminal, a claim that even center-left Vox had to agree with.
Nor is it likely to criticize Brzezinski’s own record promoting Operation Cyclone, the massive, multi billion dollar program to arm Islamic extremists in Afghanistan as fighters against the Soviet Union, a program now widely regarded as exemplifying the blowback phenomenon where former allies turn against the state actor sponsoring them.
Indeed, as I write this, Project Syndicate is busy defending Saudi Arabia’s war in Yemen, with an editorial by Ali Al Shihabi, the “executive director of the Arabia Foundation, a new think tank that will focus on the geopolitics of the Arabian Peninsula”. Al Shihabi has calmly reassuring words for those disturbed by attacks such as the bombing of a funeral ceremony which led to 140 deaths. Totaling up the human cost of the war so far, he concludes: “For an air campaign waged for nearly two years against an unconventional army, this figure is not particularly high.”
That is not to say that Project Syndicate is a right-wing site. Far from it, its columns tend to occupy the center-left to center-right, to borrow a phrase from Hillary Clinton, and that’s following a more international definition of “centrism” than the right-leaning US version.
For example, PS created a special focus section on Donald Trump called “Trump: An American Horror Story”, and the site frequently reports on environmental issues and the international efforts to combat climate change. Here, too, it tends to follow more of a Hillary Clinton vision than a Bernie Sanders one, promoting fracking through several stories including, of course, one by Lomborg, who predictably calls it “this decade’s best green-energy option”.
In fairness, the credentialist centrism that defines Project Syndicate does leave room for a lot of sensible voices, including leaders of various NGOs and generally reasonable politicians arguing for peace, democracy, and apple pie. It has even given plenty of space to prolific progressive firebrand Yanis Varoufakis. But Jeffrey Sachs, who’s stuck with the project the longest as its first monthly columnist, is perhaps the best example of this benevolent form of punditry, the elite-friendly “how about we try this crazy thing” mentality that actually sometimes leads to positive agendas being implemented.
Project Syndicate content is licensed under conventional copyright – the newspaper subscriber model depends on at least some subscribers paying for the content. That said, the content is available online, sometimes in abbreviated form that requires logging in. There’s a small discussion section below each story, which usually receives a small to moderate amount of activity. There is no prominently noted way to submit corrections for any story.
The Verdict
Although non-profit, Project Syndicate is effectively mainly funded by for-profit media. It amplifies the perspective of elite voices across all sectors of society, while concealing conflicts of interest. The lack of obvious disclosure even regarding writers whose organizations are funders of the project, and the use of PR blurbs like Tony Blair’s, is especially iffy.
The bias towards credentialism is likely good for continuing to attract foundation funding and subscribers, but it doesn’t in fact engender a diverse set of perspectives. The Conversation, previously reviewed here, is a more inclusive alternative, in spite of its own selective focus on voices within academia.
Until Project Syndicate addresses some of its transparency deficits and manages to pivot towards a broader definition of “the greatest minds” with less emphasis on credentialism and increased focus on marginalized and underrepresented voices, I cannot recommend it as a source of analysis.
Nevertheless, I personally do follow Project Syndicate on Twitter to get a window into what views are being promoted by elites around the world, but it’s especially important to read it critically and conduct one’s own investigations of an author’s motivations and opposing viewpoints. Three out of five stars.
The Conversation may well be the most remarkable news site you’ve never heard of. After a start in Australia in 2010, the site has since added five editions: UK, the US, Africa, France, and a Global edition. The premise is simple enough: academics, researchers, and PhD students write news backgrounders, special reports, and explainers for complex topics, targeting a general audience. Readers are encouraged to engage in discussion with clearly stated and enforced community standards – and authors frequently participate in those conversations, as well.
The whole operation is fully non-profit, with funding that comes primarily from a large array of foundations and participating academic institutions. The most recent available tax return for the US edition, which is only 2 years old, notes about $2.3M in annual revenue, but The Conversation Media Group in Australia from which it spun off is a separate entity.
With a network of more than 36,000 writers, the scale of this project is staggering. These authors write in partnership with professional journalists who are part of the Conversation team. All content is under the Creative Commons Attribution/No-Derivatives License, which allows free republication without modifications, including commercial re-use. Because many sites do pick up their content, The Conversation’s reach extends well beyond the 3.7 million monthly users that go to the site directly.
The website runs on a custom content management system which is proprietary and likely to remain so. It is is quite well-designed: pages load fast, the multi-column layout is easy on the eye, the navigation makes sense, and it’s mobile-friendly. The commenting system is one of their own creation which, as of this writing, lacks functionality to edit one’s own comments but is otherwise easy to use.
Each edition has its own Twitter/Facebook/RSS feeds, so in order to get a mix of global and US posts, for example, you can just subscribe to both feeds.
So, what’s the content like? If you’re familiar with Vox.com, think of The Conversation as a less sensationalist version that is more careful with the facts while serving up more diverse views from around the world. Alongside lots of mundane stuff (the US frontpage article right now is “How making fun weekend plans can actually ruin your weekend”), that includes radical perspectives from time to time when they can be found in academia, such as articles by Greek academic and progressive firebrand Yanis Varoufakis.
And it also includes charming articles like How majority voting betrayed voters again in 2016, where a French mathematician advocates that the US should immediately adopt a voting method for presidential elections called “majority judgment” he and a colleague have devised. (The argument is interesting enough, but without grounding in any kind of political reality it is indeed a purely academic one.)
Consistent with standards in academic publishing, authors must disclose conflicts of interest and “relevant affiliations”, making it harder for the site to act as a conduit for advocacy by special interests.
All articles I’ve read meet a certain minimum bar of quality (they make an effort to engage the reader, they’re accurate and clear), but the ceiling varies considerably. In quite a few cases, you’d be better off heading over to Wikipedia to understand a subject, not because the backgrounder by The Conversation is wrong, but because it just consists of a few links and some fairly banal observations. Still, the site is (in my view) vastly preferable to commercial offerings like Vox because it publishes a truly diverse and increasingly global community of authors.
The Verdict
The Conversation is unique, and the site’s founders deserve credit for realizing a bold vision of a non-profit platform that helps us engage in smarter conversations with each other about the world we live in. Whatever your political views, I suggest adding one or more of their feeds to your news mix to sample their content.
If I could pick one area for the site to improve in, it would be to focus more on truly excellent journalism at the expense of sheer volume. Beyond that, a stronger commitment to open source values (opening up the platform, engaging the community in governance issues, using a more permissive license for the content) would be lovely to see. 4 out of 5 stars.
Não é preciso ser especialista em comunicação para atestar o óbvio: a grande mídia no Brasil é controlada por poucas famílias, milionárias e com um interesse premente na manutenção do status quo. Muito do que se chama de “opinião pública” nada mais é que o eco dos mesmos jornalistas, sempre com a mesma agenda liberalizante e sob um cínico véu de imparcialidade. É nesse contexto que pequenas publicações como o Outras Palavras se fazem necessários.
O Outras Palavras é uma plataforma com uma perspectiva de esquerda, e conta com uma riquíssima gama de temas, da economia às artes e da política à tecnologia. Nenhuma temática é imune de problematização, e isso inclui a própria esquerda, que é frequentemente autocriticada.
O site, que ostenta uma licença Creative Commons BY-SA, republica textos de outros autores, traduz peças de pensadores contemporâneos e cria conteúdo original, numa mistura bastante abrangente e interessante. É um dos poucos veículos de esquerda que não insistem no governismo tosco típico da Carta Capital, por exemplo, ou que sentem nostalgia por experimentos socialistas fracassados, como o vermelho.org.br.
Quanto à sua independência financeira, cabe aqui ressaltar uma informação importante sobre como o portal é financiado:
Em 2015, os leitores contribuíram com R$ 140 mil – o que correspondeu a 71% de nossas despesas. Em 2016, planejamos gastar R$ 238,8 mil […]. Deste total, R$ 210 mil – ou 87,5% – virão de contribuições solidárias, por meio de Outros Quinhentos.
Recomendo a todos que desejam estar a par dos acontecimentos recentes do mundo, sempre com um olhar afiado e crítico.
In 2008, journalist and author Bill Bishop co-authored The Big Sort: Why the Clustering of Like-Minded America is Tearing Us Apart. It examines how communities across the US are becoming more politically one-sided. This isn’t just a Kentucky vs. California thing – within these states, you’ll find increasingly sharp political divisions. Part of the reason is that people like to live with others who think like them: they “sort” into communities that reflect their values.
In this climate of polarization, it can become easy to fall into stereotypes, and to lose sight of common concerns that all communities share: jobs, access to health care, working infrastructure, clean water and clean air, and so on. Bishop is also a journalist and the co-founding editor (with his wife) of the Daily Yonder, a website that focuses specifically on the needs of rural communities. As such, it also seeks to overcome stereotypes and help people see the diversity of rural America.
The Daily Yonder is published by the Center for Rural Strategies, a non-profit based in Whitesburg, Kentucky, and Knoxville, Tennessee. The Center had about $832K in revenue in 2014, much of it from well-established foundations like the W.K. Kellogg Foundation (yes, named for the guy who founded the cereal company) and the Nathan Cummings Foundation. Although there’s a big fundraising button on every page, individual or small organization contributions average to only about $20K a year.
Its reach can only be described as tiny at this point: The publication has about 3,500 followers on Twitter and another 3,500 on Facebook (the Facebook page is more regularly updated); its traffic rank is similarly underwhelming. There are some self-inflicted reasons for this: once you get past the frontpage, it’s easy to get lost in the laundry list of topics and inscrutable headlines without any kind of content preview. If clickbait is one extreme of how to present news and analysis, the Yonder is close to the other end.
This also shows a fundamental challenge covering “rural America” as a whole: it’s big, and it’s hard to make local stories exciting for people who aren’t from that specific part of the country. Right now, the frontpage tells me in large letters: “DYNAMIC DELTA LEADERS: EDUCATION IS THE KEY”. Is that a story I want to read? Who knows!
But if you dig, there is lots of good content here. The Viewfinder series, for example, showcases rural photography. The In the Black series is a column that relates the experiences of an underground coal miner. Beyond Coal examines the transition from fossil fuel to renewable energy. The “Speak your piece” columns reflect on many aspects of rural life while staying clear of the vitriol that has become a mainstay of US politics.
Bill Bishop himself followed up on his “The Big Sort” analysis with an insightful article that examines the rapidly increasing percentage of voters who live in “landslide counties” where one of the two parties is likely to win a presidential election with large margins.
Each story has a small Disqus-enabled section for comments, though few stories attract significant discussion. The content is under conventional copyright, and some is syndicated from other sources.
The Verdict
The Daily Yonder deserves to exist, because it provides a much-needed journalistic perspective on rural America. But to truly reach people (rural or not), it will need to strive to become a more engaging source that can successfully perform the difficult task of translating local experiences into public interest journalism with broad appeal to readers in different parts of the country. Because it falls short of that potential, I give it 3 out of 5 stars. If you are interested in authentic perspectives on rural America, I do nevertheless recommend liking their Facebook page or subscribing to their RSS feeds as a way to keep up with their important work.
Jacobin is a New York based socialist quarterly magazine founded by Bhaskar Sunkara when he was 21 years old. It was started online in 2010 and is now also in print, with some content only available to subscribers of either edition. The website features news and analysis on an ongoing basis.
Sunkara is also a vice-chair of the Democratic Socialists of America, and he takes the “democratic” part seriously (“Any socialism we build will need to have a free, open civil society and multiparty democracy”, he recently tweeted). At the same time, you will find in Jacobin a perspective that is deeply critical of US mainline politics. On Bernie Sanders’ run, Sunkara predicted that Sanders would lose in the primaries, but that his run could be “an opportunity for movement building”.
In an interview with New Left Review, Sunkara articulated this focus on movement-building as core to his political philosophy: “What’s needed is to build movements until we reach a point where electoral options are actually viable.”
The organization behind Jacobin is a non-profit with about $300K in revenue in 2014. There is no Annual Report, which is not surprising for a tiny organization. In the aforementioned interview, Sunkara stated that most of this revenue is from subscriptions, with donations accounting for about 20% of the budget. In spite of its political radicalism, Jacobin is under conventional copyright terms (including back issues), and offers no discussion forums or other interactive components.
The print issue of Jacobin contains in-depth articles alongside beautiful graphic design (example issue). Unlike quite a few leftist magazines, Jacobin doesn’t engage in a lot of postmodernist piffle; its articles are often supported by charts and data, and tend to share a focus on issues that have real world relevance, including occasional departures into sci/tech themes like 3D printing or Silicon Valley politics.
So what can we find here that’s not reported elsewhere? Here are a few examples:
- an in-depth analysis of the prospects of the Kurds in Turkey, written by Djene Bajalan, an assistant professor with focus on Middle Eastern affairs
- a reasonable critique of Chuck Schumer, the prospective Democratic minority leader in the US Senate
- an analysis of the US media industry and the impact of the profit motive by Annenberg media studies scholar Victor Pickard.
One might wonder how a socialist magazine treats left-wing authoritarians. Will it applaud or rationalize as they restrict speech and political freedom, or will it criticize? The coverage of Cuban dictator Fidel Castro and Venezuela’s elected authoritarian Nicolás Maduro give us some idea. The Jacobin Castro obituary is in fact one of the better ones I’ve read, and is unambiguous in its criticism, for example:
“It was relatively simple to dismiss the calls for democracy from internal critics as imperialist propaganda, rather than a legitimate claim by working people that a socialism worthy of its name should transform them into the subjects of their own history. Public information was available only in the impenetrable form of the state newspaper Granma, and state institutions at every level were little more than channels for the communication of the leadership’s decisions.”
“An opaque bureaucracy, accountable to itself alone, with privileged access to goods and services, became increasingly corrupt in the context of an economy reduced to its minimal provisions. Castro’s occasional calls for ‘rectification’ removed some problem individuals but left the system intact.”
It concludes that “any socialism worth its name needs a deep and radical democracy.”
Jacobin’s coverage of Venezuela’s dysfunctional, corrupt and increasingly authoritarian government has been less robust and more likely to look for justifications primarily in the behavior of the right-wing opposition, though the article “Why ‘Twenty-First-Century Socialism’ Failed” by Venezuela-born socialist Eva María offers a more critical perspective which echoes the commitment to worker-focused democracy that defines Jacobin’s politics:
“The party, however, did not rely on its members’ active participation no matter how much Chávez liked to say it did. Instead, a bureaucratic structure, where criticism, open debates, and rank-and-file power were more often the exception than the rule, took over. The party formalized the bureaucratic layer of nominal Chavistas who were put in charge of different state sectors. In no time, this new caste engaged in corrupt behavior while continuing to deploy socialist rhetoric. The government’s ideas of funding and supporting popular power didn’t work in practice.”
The Verdict
Operating on a tiny budget, Jacobin offers a much-needed, intellectually coherent journalistic challenge to the prevailing social and economic order. The pitfalls of its political position are easy to pinpoint: the history of socialism and communism is riddled with failed economies, brutal autocrats and centralized bureaucracies, which calls into question whether its aspirations can ever be achieved in practice.
To build a mass movement for democratic socialism in the United States may seem like the remotest of possibilities, but the political successes of Bernie Sanders and the failure of the Democratic party to protect the progressive gains it has made under the Obama administration will lead many young people to search for alternatives.
Whether Jacobin can be a leading voice of that search for alternatives (within the two-party system, or outside mainline politics) will largely depend on whether it can maintain its commitment to a vision of radical democracy, consistently oppose political violence, and overcome any impulse to jump to the defense of authoritarian leaders who share some political objectives. The left is not immune to group polarization, and unreconstructed old-school socialists who habitually defend the indefensible are the political anchor around its neck.
I recommend Jacobin with reservations: read critically, it offers a useful complement to anyone’s diet of news and analysis. It is also aesthetically pleasing and edited with care, and their Twitter account is a good way to follow their work. 3.5 out of 5 stars, rounded up.