Reviews by Eloquence
After a long, bloody history of colonial rule, Britain finally abandoned in the Indian subcontinent in 1947. Against significant opposition, the Brits negotiated the partition of India into India and Pakistan. This led to a refugee crisis, mass violence, and the deaths of between 200,000 and 2 million human beings. The resulting so-called “Muslim homeland” of Pakistan was not the nation we know today, but a country divided into West Pakistan and East Pakistan, with a whole lot of India between them:
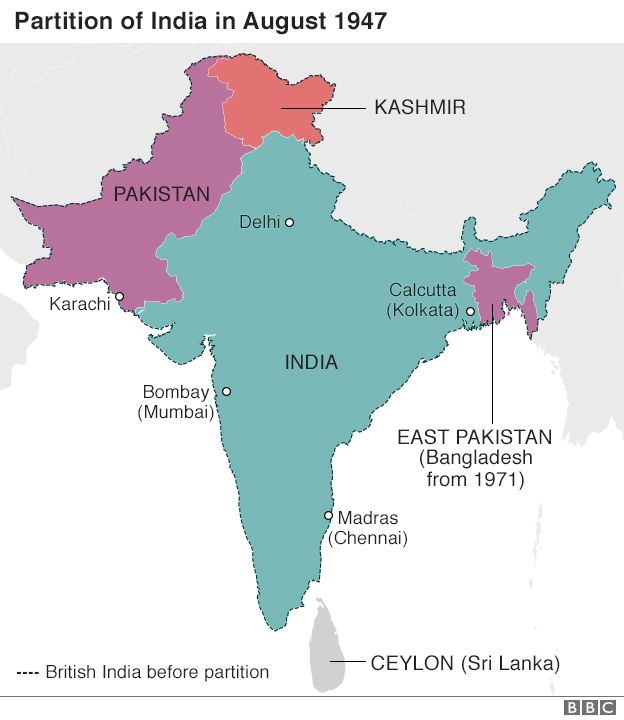
Partition resulted in a bizarre post-colonial map, with a divided “Muslim homeland” (home to millions of non-Muslims) bordering India. Credit: BBC. Fair use.
Less than 30 years later, the fiction of East Pakistan collapsed in genocide and war. After an election that would have shifted the balance of power to the Awami League, which sought independence for the East, Pakistan responded by abandoning its brief experiment with democracy and sent in its troops from the West. They unleashed atrocities that killed between 300,000 and 3 million people (often with weapons Pakistan had bought from the US). Hindus were singled out for extermination and expulsion, making this a genocide by every definition.
This spurred a refugee crisis that overwhelmed neighboring India, giving it cause and pretext to arm its Bengali neighbors and, ultimately, help them fight the Bangladesh Liberation War. The country of Bangladesh was born from the blood and the ashes. Brutal revenge killings against anyone who was seen as a collaborator with the Pakistani military followed.
The Blood Telegram by Gary J. Bass tells this story with special focus on the actions of US foreign policy decision-makers, chiefly Richard Nixon and Henry Kissinger. Nixon had developed a personal friendship with Pakistan’s dictator, Yahya Khan, and sought to preserve a strategic alliance with Pakistan, in part in order to use Yahya as a secret diplomatic channel in the planned opening of relations with the People’s Republic of China.
Bass uses the Nixon White House tapes, interviews, and countless historical documents to reconstruct a detailed picture of how the US government and its foreign policy apparatus responded to the genocide as it unfolded in East Pakistan.
A very clear picture emerges: Nixon and Kissinger did not care about the genocide, declined to put any pressure on Yahya to stop it, and bullied internal dissenters into silence. They refused to stop all pending arms transfers, and when the Bangladesh Liberation War started, they illegally used third countries (Iran, still ruled by the US-backed Shah, and Jordan) to funnel weapons to Pakistan. They tried to draw China more deeply into the conflict, and threatened India with an aircraft carrier.
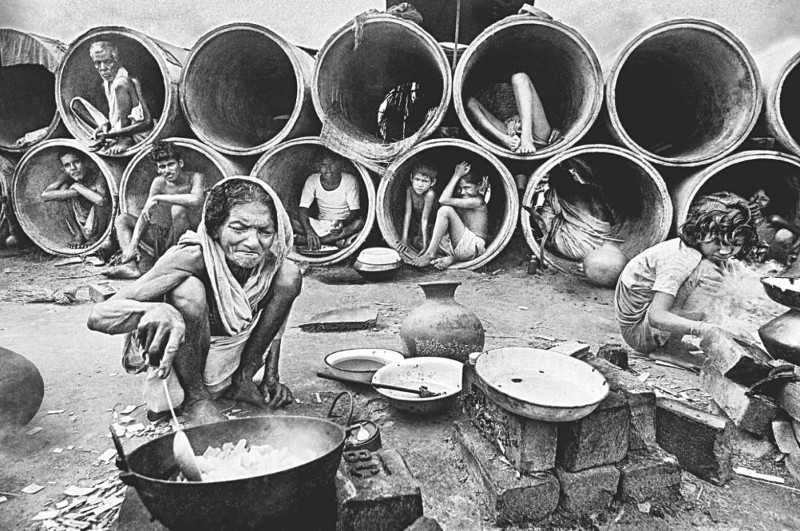

“Salt Lake” refugee camp in Calcutta. Millions of refugees from the genocide overwhelmed India, a country already struggling with extreme poverty. (Credit: Raghu Rai. Fair use.)
“Our government has failed”
The “Blood Telegram” of the title was sent by Archer Blood, then US Consul General in Dacca soon after the genocide started. The diplomatic staff were witnessing the mass killings firsthand, and after repeatedly warning their superiors about the unfolding crisis, they prepared a confidential dissent statement to express their deep concern with US foreign policy.

Excerpt from the “Blood Telegram” itself, April 6, 1971.
Blood did not sign the statement, but he expressed his agreement with its contents. For his dissent, Nixon and Kissinger recalled him to the State Department’s personnel office back in DC.
Even in isolation, any defense of US foreign policy towards the 1971 genocide does not withstand scrutiny. There was no “pragmatism” here, because the US did not pragmatically push for political stability when it had the opportunity to, nor did it pragmatically choose one of the many alternatives for creating an opening with China.
Bass shows the role of emotion and prejudice in decision-making. Kissinger, who cultivates an image of a wise statesman and master of “realpolitik”, was ranting and raving about the Indians along with Nixon, and the two of them outdid each other with bizarre analogies (Yahya was “Lincoln”, the Indians were “Nazis”, Pakistan was being “raped” by India). The best that can be said about their actions is that they provided (inadequate) humanitarian aid to India in a “too little, too late” attempt to avert or delay war.
One fascinating aspect of this history is the role of the Soviet Union. An authoritarian regime, it allied itself with democratic India and supported the liberation of Bangladesh. In a complete reversal of Cold War stereotypes, here it was the Soviets who defended democracy and human rights, for their own reasons that were far more cool and pragmatic than Nixon’s emotional allegiance to a military dictatorship that pursued a course of self-destruction.
An incomplete portrait
The Blood Telegram is neither a full accounting of the events that led to the creation of Bangladesh, nor a comprehensive view of America’s foreign policy under Richard Nixon and Henry Kissinger. While Bass hints at other evils—the brutal escalation of the Vietnam War, the carpet-bombing of Cambodia, the installation of a murderous dictatorship in Chile—he focuses on his central thesis: different choices could have prevented or slowed the killing in East Pakistan.
Bass makes this case with commendable scholarly rigor, but an obsessive level of detail about the Nixon/Kissinger dynamic takes up space that could have been used to place these events in their larger context. In isolation, America’s complicity in the genocide in East Pakistan may seem like a historical abnormality. In the larger history of US foreign policy, which is littered with millions of avoidable deaths, it’s not the specific behavior of Nixon and Kissinger that was historically abnormal, but the vocal dissent represented by the Blood Telegram.
Homo sapiens spent 99% of its existence on Earth in a hunter-gatherer lifestyle. So it’s perhaps no surprise that the game Don’t Starve, where you gather twigs and berries and set traps for rabbits, has an incredibly addictive quality to it. Released by Canadian indie studio Klei Entertainment in 2013, Don’t Starve has since spawned a multiplayer variant and a fair amount of downloadable content (DLC).
The base game will keep you busy for a while. It combines roguelike elements (procedurally generated worlds) with crafting, farming, a day/night cycle, seasons, and many different ways to die.
For starters, there’s darkness itself: if you spend more than a few seconds in total darkness, you will die from mysterious causes. If you don’t eat, you starve (duh!). If you don’t find ways to preserve your food, it slowly spoils in your inventory. If you don’t sleep, you slowly go insane. Every few nights you get attacked by ever-growing packs of hounds. During winter, you may freeze to death. Or you could get killed by bees, frogs, spiders, giant birds, tentacles, pengulls, beefalo, did I mention tentacles, and myriad other creatures.
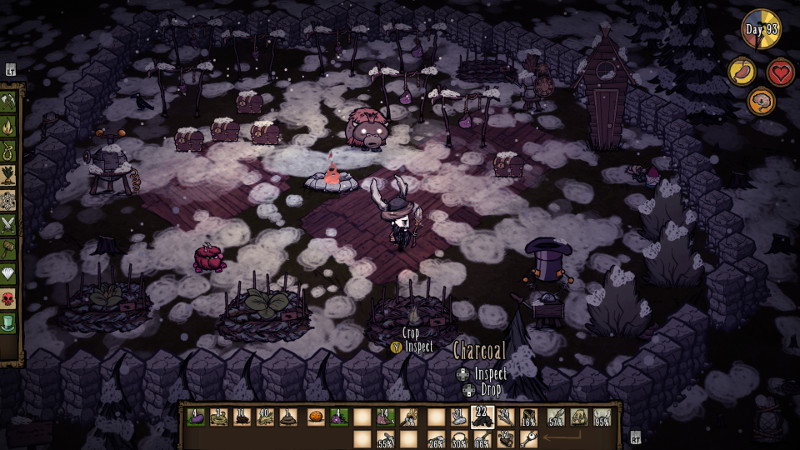
A small walled camp with a tamed baby beefalo, farms, and drying racks for meat. (Credit: Klei Entertainment. Fair use.)
Still, after a few early deaths (and maybe after reading a few spoilers online), the game becomes surprisingly chill. Most creatures don’t attack unless provoked or approached, and you can craft yourself a little fortress and prepare a good defense against the regular hound attacks. Just as you’ve gotten the hang of it, Don’t Starve lures you into Adventure Mode, where you get to face off against the game’s antagonist, a pinstripe-wearing half-demon named Maxwell, in extra-hard challenge worlds.
You also quickly unlock most of the game’s playable characters, all with different skills and weaknesses. So far I’ve mostly played as Wilson, but I look forward to playing as creepy-girl-with-the-dead-sister Wendy or as Woodie, a lumberjack with a talking axe.
As you may have guessed by now, the game does not go for realism: its art style is influenced by Tim Burton, and its world is littered with magical items and the means to craft them. You will also encounter sentient pig creatures living in little houses, who can be tamed to do your bidding, or brutally killed and turned into football helmets and meat.
Procedural generation works best if it creates worlds that feel like places worth visiting, not just empty rooms and corridors. Each game world in Don’t Starve is a place to be navigated: where are the rocks to mine, the berries to harvest, the trees to fell? As you survive days and nights, your brain starts to map out these game worlds just like it does any other place.
The Verdict
Don’t Starve is a masterclass in game design, with excellent controls and menus that make the complexity of its mechanics a joy to manage. While I didn’t find the artwork very appealing at first, it quickly grew on me, thanks to lighting and sound effects, cute animations and funny dialogs, and the living rhythm of the game’s plants and creatures.
The game has its dull moments where you just gather resources or wait for night to turn into day. But these quiet minutes also present opportunities to organize your inventory, to craft a needed item, or to plan out the next day.
Don’t Starve is available for virtually every platform now (including Linux, Android, and Nintendo Switch), and you can regularly find the Steam or GOG version on sale for $5 or less. Developer Klei Entertainment also deserves credit for publicly renouncing “crunch time” and pledging not to overwork its developers. I highly recommend the game, and I look forward to checking out Klei’s other titles, nearly all of which have received very favorable reviews.
I’m a big fan of point and click adventures (think The Secret of Monkey Island), a genre that’s frequently been declared dead but that is in fact thriving thanks to crowdfunded major efforts like Broken Age (reviews) and Thimbleweed Park (reviews), smaller studios like Wadjet Eye, and releases by even smaller teams or solo developers. Clam Man is very much the latter, developed by “Team Clam” which appears to comprise three collaborators.
The game is set in a world dominated by anthropomorphic aquatic creatures. You play Clam Man, an ordinary bloke working as a junior sales representative at Snacky Bay Prime Mayonnaise. After Clam Man gets fired for no apparent reason by his crab boss, he begins to uncover a larger mayo-centered conspiracy. Does it go all the way to the top? Mr. Man will try to find out.

Not all is as it seems at Snacky Bay Prime Mayonnaise. (Credit: Team Clam. Fair use.)
It’s all ridiculous, of course, but some of the jokes are quite funny, and the minimalist hand-drawn art is often very charming. This is only a two hour game, the mouse controls are a bit frustrating, and the writing and artwork don’t quite hold up throughout the short playtime, so the current asking price of $10 is a bit high.
If you already own the game from The Mother of All Bundles, or if you can get it for $5 or less, you’re unlikely to regret your visit to Snacky Bay. Team Clam is certainly one indie developer to keep an eye on.
A Short Hike lets you explore the colorful, pixelated world of Hawk Peak Provincial Park in the role of a vacationing anthropomorphic bird named Claire. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to make it to the top of Hawk Peak, ostensibly in search of cell phone reception.
As you make your way through the park, you meet a diverse cast of animal characters. Some offer you side quests, others are simply pursuing their own adventures in the park. It’s up to you whether you want to accept any of these quests, but if you want to make it to the peak, you’ll need to at least obtain a few golden feathers, which allow you to climb the distance.
The game doesn’t end after you reach the peak. There are treasures to be found, hats to be purchased, fish to be caught, and co-operative games of beachstickball to be played. And it’s fun to explore. In spite of the intentionally low resolution graphics, when you sky-dive from the top of a hill, A Short Hike manages to convey a real sense of velocity and freedom.

You can fly, dive, swim, climb, walk, and run. (Credit: Adam Robinson-Yu. Fair use.)
You can’t die in this world, or screw up in any irreversible way. Nor does the game offer the endless grind of more complex farming, fishing, and crafting games. You can rush through the game, or spend a few hours with it, but after that, you’ll likely be done with it—at least until you feel like paying another visit to the park.
If you’re looking for a game to challenge your reflexes or your logic, this ain’t it. But if you just want to chill in a beautiful setting, it’s a perfect pick-me-up.
In Some Assembly Required, biologist Neil Shubin explores a theme he already touched upon in his 2008 book Your Inner Fish and the 2014 PBS documentary of the same name: How do complex bodies, with all their specialized functions, evolve? How does evolution build on that which has come before?
To answer these questions, Shubin revisits the discoveries of biologists and naturalists of the past and introduces some of the most recent findings of molecular biology. This is a popular science book, so scientific facts become stories whose protagonists are brought to life with biographical detail.
The key concepts Shubin introduces include:
-
how biological traits that have evolved for one function are re-purposed (exapted) for another (e.g., feathers likely evolved first for temperature regulation, then were exapted for flight);
-
how small changes in embryonic development can have dramatic effects on the resulting individual—e.g., the slowing of physiological development known as neoteny, where adults may retain traits otherwise only seen in the young;
-
how gene duplication events (e.g., via self-copying genes known as transposons or “jumping genes”) enable evolution to experiment with myriad small variations of existing genetic recipes, which has led to vast gene and protein families;
-
how plant and animal cells incorporated previously free-living organisms and thereby gained crucial new capabilities, the classic examples being mitochondria (the powerhouses of animal cells) and chloroplasts (the photosynthesis engines of plant cells);
-
how viral elements have made their way into our DNA and have been co-opted for important biological functions (e.g., to make the protein syncytin, which is a key component of the placental barrier between fetus and mother).
Shubin explains how evolution often arrives at the same solution multiple times, with different genetic origins, and illuminates why some evolutionary pathways are likelier than others.
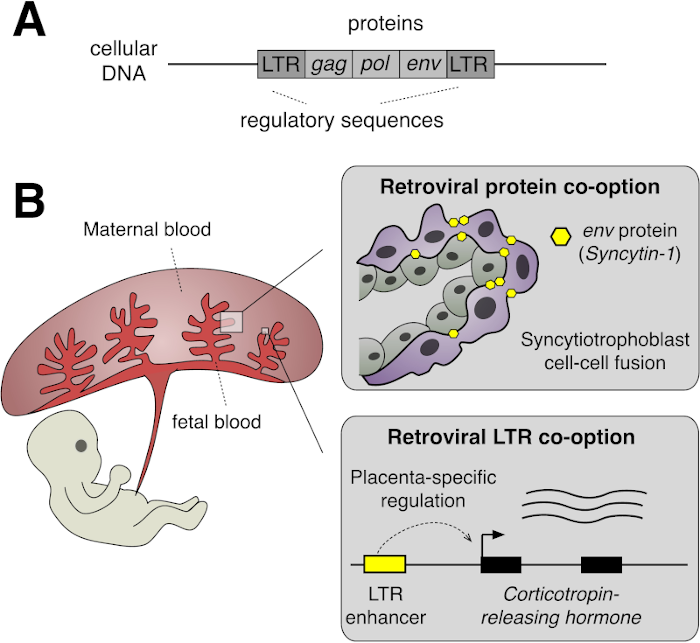
A retrovirus upon integration in the host genome (A), where its genetic code has been co-opted for building a protein used in placental development (B, top), and for the regulation of birth timing (B, bottom). (Credit: PLOS Biology / Edward B. Chuong. License: CC-BY.)
The book only scratches the surface of these concepts, and much of what it does cover is likely to be well-trodden ground for readers who have picked up a book about evolutionary biology since their school days. At the end of each chapter, I found myself hungry for more detail.
To Shubin’s credit, in the final section of the book, he provides a kind of afterword for each chapter, which includes sources and additional reading recommendations. I found this approach much more useful than a conventional bibliography or a set of disjointed footnotes.
I would give this book 4 stars — it’s a light, quick and engaging read on a fascinating topic. For readers looking for more breadth or more depth, I would recommend the following writers:
-
Richard Dawkins, if you are not put off by his politics, is still one of the best science writers I know. The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution (2009; reviews) is a passionate, detailed and eloquent introduction to evolutionary biology.
-
Nessa Carey has a remarkable talent for getting as close to the science as possible while still writing for a lay audience. I read The Epigenetics Revolution (2012) and was deeply impressed by her clarity and ability to break down very complex concepts.
-
Andreas Wagner is a biologist bringing his own ideas to a larger audience through popular science writing. If the science behind it withstands scrutiny, Arrival of the Fittest (2014; reviews) could well be turned into a new chapter in the next edition of Some Assembly Required.
In short, Wagner argues that in order to find new functions for old genes, evolution has to take a “genetic walk” from A (old function) to B (new function). He explains the importance of neutral mutations in these genetic walks. His latest book, Life Finds a Way: What Evolution Teaches Us About Creativity, looks similarly fascinating.
If you’re on the fence about Some Assembly Required, consider getting a copy of the PBS documentary Your Inner Fish. It showcases Shubin’s storytelling talent while still packing a good amount of science. If you enjoy it, you’re unlikely to be disappointed by Some Assembly Required.
A Normal Lost Phone (reviews) by Accidental Queens allowed the player to explore a simulated smartphone to discover what happened to its owner, an 18-year-old named Sam. Another Lost Phone uses the same idea to explore different themes. This time, the phone in question belongs to a woman named Laura, who has apparently gone missing.
SMS messages reveal that her boyfriend, Ben, is deeply concerned about her disappearance—but some of his earlier messages suggest a controlling personality, hinting at another story to be uncovered.
The story is told through messages, photos, emails, calendar entries, and notes, many of which are only accessible until you’ve figured out a password or PIN number through various clues. Most of these puzzles are pretty easy, but if you find yourself getting stuck, the excellent Steam Guide will help you to advance without any spoilers.
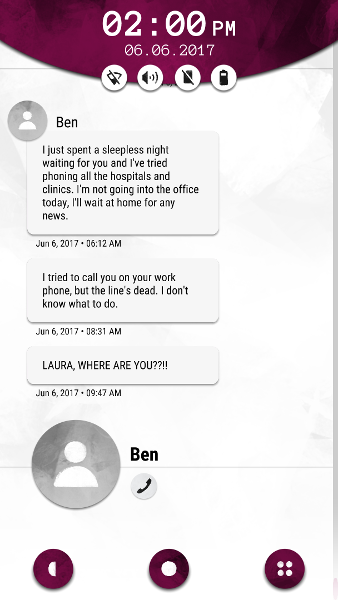
The first messages we see are from Laura’s boyfriend Ben, expressing deep concern about her disappearance. (Credit: Accidental Queens. Fair use.)
Like the first game, Another Lost Phone explores sensitive social topics with appropriate care, if you can get past the inherently voyeuristic storytelling device of exploring a stranger’s phone.
The game feels a bit more polished than A Normal Lost Phone, with a more engaging story, where all the different pieces (messages and clues) click together really well. Each game tells its own independent story, and if you’re unsure which one to try first, I recommend this one. My playtime was about 1-2 hours.
I lived in the San Francisco Bay Area from 2008 to 2015. One name that you’ll encounter sooner or later in this region of the United States is Junípero Serra: from Junipero Serra Freeway to Junipero Serra Boulevard, from schools to playgrounds, from hiking trails to the highest mountain peak in Monterey County, and of course the statues—so many statues.
Canonized as a saint in 2015, Serra was an 18th century priest and friar who founded the first Spanish missions in California. Pope Francis claimed that Serra “sought to defend the dignity of the native community, to protect it from those who had mistreated and abused it.” The missions Serra started are popular tourist attractions.
In 2004, Elias Castillo (1939-2020), a journalist and three-time Pulitzer Prize nominee, wrote an op-ed titled “The dark, terrible secret of California’s missions” that described Serra’s work in starkly different terms:
[L]ocked within the missions is a terrible truth—that they were little more than concentration camps where California’s Indians were beaten, whipped, maimed, burned, tortured and virtually exterminated by the friars.
The op-ed was well-received by others familiar with this history, and was read into the Congressional Record. This inspired Castillo to write the book A Cross of Thorns: The Enslavement of California’s Indians by the Spanish Missions (2015).
Castillo documents that Serra was a reactionary even by 18th century standards, a man who believed in witches, rejected Copernicus, practiced extreme self-flagellation, and regarded the natives of California as savages who had to be enslaved to be brought to salvation.

Yokuts hunting near San Francisco Bay as depicted by Russian artist Ludwig Chloris. (Public domain)
Fever dreams of salvation
Natives were herded into the missions and were forcibly returned there if they tried to flee. They lived in conditions of forced labour, and died by the thousands, often from disease which ran rampant due to the high population density. Far from “protecting” the natives, Serra resisted efforts to reduce the rate of death, to provide education or better care.
Instead of education, there was daily mass in Latin, which the natives did not understand. The Church enforced its sexual morality, separated men from women, and punished expressions of intense emotion, including grief. In a 1780 letter to Felipe de Neve, then governor of the Californias, Serra justified the use of flogging:
“That spiritual fathers should punish their sons, the Indians, with blows appears to be as old as the conquest of these kingdoms [the Americas]; so general in fact that the saints do not seem to be any exception to the rule. In the life of Saint Francis Solano … we read that, while he had a special gift from God to soften the ferocity of the most barbarous by the sweetness of his presence and words, nevertheless … when they failed to carry out his orders, he gave directions for his Indians to be whipped.”
Castillo’s book is unsparing but rigorous and well-sourced, often in the words of the people who committed these crimes or witnessed them. The many dedications to Serra in California are honoring a mass murderer. His canonization will forever taint the record of Pope Francis, who is often celebrated as a reformer.
In the wake of calls for racial justice in 2020, this history is becoming more widely known, and the first Serra statues are being removed. The myth of the friendly California missions has no place in the 21st century, and Castillo’s book should help us all to put it to rest.
Additional reading
-
Junípero Serra’s brutal story in spotlight as pope prepares for canonisation
The Guardian, September 23, 2015 -
Junipero Serra was a brutal colonialist. So why did Pope Francis just make him a saint?
Vox, September 24, 2015 -
‘By Their Fruit They Will Be Known’: Junipero Serra as Indian Killer
Indian Country Today, October 14, 2015 -
Sainthood of Junípero Serra Reopens Wounds of Colonialism in California
New York Times, September 29, 2015
Your Future Self is an interactive story developed by Contortionist Games, which as of this writing is one developer, Andrew Hirst, based in Sheffield, UK. The game presents itself in a CRT aesthetic with many flicker effects, similar to Pony Island.
The premise is that you’re stuck in a time looping bubble with your future self and have to convince them not to commit an act that will kill thousands of people, but which your future self clearly considered justifiable. Every dialog choice can succeed or fail. If you ultimately don’t succeed, the loop starts again.
As you pick from different strategies to engage with “yourself”, the story unfolds. You can’t pick the exact words you want to say to yourself—your choices are always to be rational, empathetic, or assertive, and the game decides what that means in a given context.
There’s a light RPG-like mechanic at play here, where your “skill” at being rational, empathetic, or assertive is measured against your future self’s skills and receptivity in those areas. If you turned on “helper mode” on the start screen, the game shows you the likelihood that a given choice will succeed.
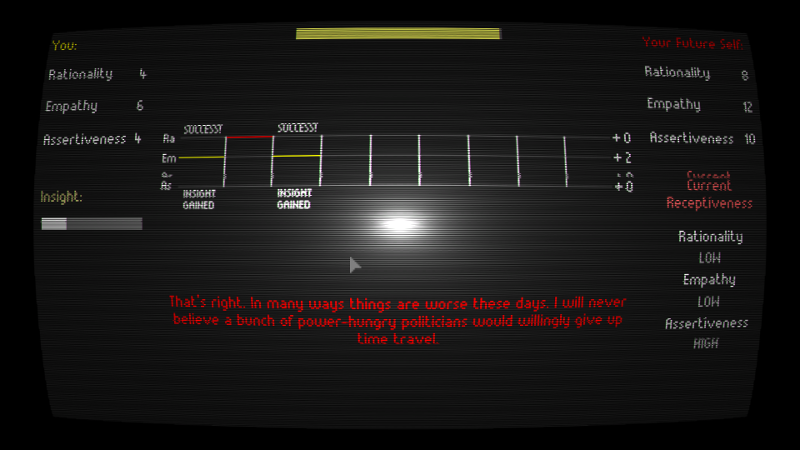
The success or failure of your attempts to persuade your future self is visualized, and is subject to a simple RPG-like mechanic. The CRT scanline effect, curved screen, and center glare are in-game visuals. (Credit: Contortionist Games. Fair use.)
There are, of course, additional layers to the story, and the game employs intense visual effects to keep things interesting. It also has an excellent chiptune soundtrack. Check out Rebels to the Rescue and Your Future Self (Remix).
The time loop mechanic can get a bit tedious if you have to click through the same loop a couple of times to find the right answers—in retrospect I think I would have enjoyed the game more if I had enabled “Helper mode”. The story was interesting enough to keep me engaged until the ending (I think I played for about 1-2 hours).
I’d give it 4 stars—the game mechanics and story aren’t perfect, but the excellent soundtrack and atmosphere make up for most of the game’s weaknesses.
The liberal Western narrative of the Cold War is that a flawed but well intentioned democracy (the United States) prevailed against a tyrannical regime that sought to spread its ideology throughout the world (the Soviet Union). The rest of the world is assigned bit parts in tales of proxy wars and covert ops between the superpowers.
In The Jakarta Method, journalist Vincent Bevins reveals a much darker story of the Cold War, one in which Third World nations sought independence from colonial rule and from post-colonial imperial domination by any superpower, and in which the United States and its allies countered such efforts, in part, through an international program of mass murder.
As the book’s title suggests, this history is centered on events in Indonesia, which is the 4th most populous nation on Earth today. After achieving its independence from the Dutch (whose colonial rule had left the country with a literacy rate of less than 10%), the new country’s first president, Sukarno, sought to build alliances with other Third World nations and organized the historic Bandung Conference in 1955.
A template for mass murder
Sukarno was not a communist, but he tolerated the Communist Party as one of multiple constituencies he unified under his increasingly authoritarian rule. The United States grew impatient with Sukarno’s anti-imperialism, and supported staunchly anti-communist military men who could replace him.
Eventually, one such man, Suharto, used the chaos of a failed coup attempt by other members of the military (of which he had foreknowledge) as a pretext to take power. He blamed the communists and implemented a mass murder program that killed a vast number of human beings, with estimates ranging from 500,000 victims on the low end to 2-3 million on the high end.
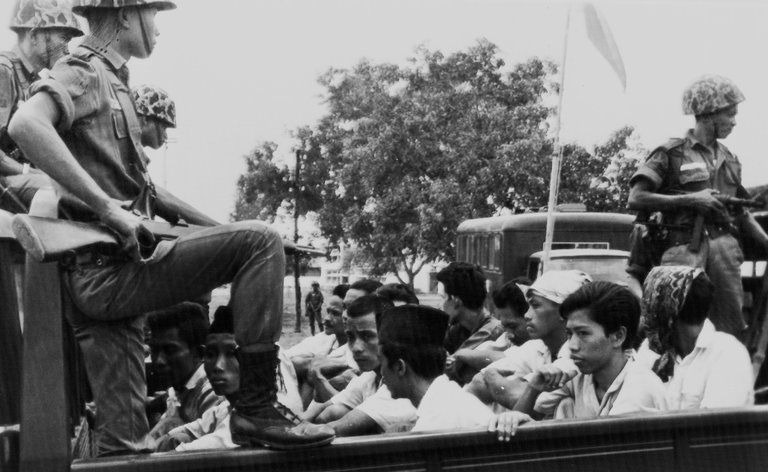

Alleged young communists detained by Indonesian troops in October 1965. (Credit: Associated Press. Fair use.)
The US did not simply tolerate this campaign; it provided training and support to anti-communists in the Indonesian military, and even supplied kill lists which were used to hunt down and murder thousands, as the Washington Post reported in 1990:
For the first time, the officials are acknowledging that they systematically compiled comprehensive lists of communist operatives, from the top echelons down to village cadres in Indonesia, the world’s fifth most populous nation. As many as 5,000 names were furnished over a period of months to the army there, and the Americans later checked off the names of those who had been killed or captured, according to the former U.S. officials.
Unlike other atrocities of the 20th century, this one remains little-known in the Western world, for obvious reasons: history is written by those who prevailed. As Bevins shows, the slaughter became a template for mass murder programs elsewhere, including in Latin America.
Before those programs began under authoritarian regimes in countries like Chile, Argentina, and Brazil, the word “Jakarta” itself was employed as a threat. Leftists and fanatical anti-communists alike knew all too well what it meant: mass murder at an unimaginable scale. Suharto had made Indonesia’s capital synonymous not with Third World emancipation, but with exterminating the political left.
Making the world safe for capitalism
The narrative of anti-communism is that all movements calling themselves socialist or communist ultimately become tyrannical, justifying the absolutist stance that the United States took in the Cold War. But the US supported murderous regimes like Suharto’s, while forcefully opposing emancipatory politics by Third World countries—no matter how democratic.
By replicating the Jakarta method around the world, the US and its allies destroyed the possibility of a moderate, democratic path to political and economic emancipation for Third World countries. The “friendly dictators” installed to exterminate the left frequently brought ruin for the rest of society, as well. Besides slaughtering hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of his own people, Indonesia’s Suharto embezzled up to $35 billion; in 2004, Transparency International ranked him as the world’s most self-enriching leader of the previous two decades.
The Jakarta Method is not a defense of communism as it existed in the 20th century. Bevins promotes no ideology and refrains from hyperbole or polemic; he simply recounts the facts, supported by the personal stories of survivors from around the world. If anything, given the secrecy of the programs Bevins writes about, many chapters in this dark history likely are yet to be illuminated.
The book reveals that the Cold War cannot be understood without the stories of the millions of people who fought for a better tomorrow, and whose lives were brutally extinguished to bequeath us the world we live in today. Not because of a choice between a greater and a lesser evil, as the liberal Cold War narrative would have us believe, but because of actions which were unspeakably evil in their own right.
You get to browse websites, read IMs and emails and explore apps, all of which reveal layers of the game’s story. (Credit: Accidental Queens / Dear Villagers. Fair use.) Many games incorporate phones you can interact with into the game; in A Normal Lost Phone, the phone is the game. With little introduction, you get to snoop around the apps and messages stored in a lost phone that supposedly belongs to a kid named Sam who just celebrated their 18th birthday.
You discover who Sam appears to be to their friends and family; as you peel away layers of clues (“which number is the password to this app?”), you also discover new layers to Sam’s story. The story is engaging and handles mature themes of tolerance and identity well, but it is a bit predictable. It’s a short game (1-3 hours, depending on how much time you spend reading every bit of flavor text).
There’s some great artwork to discover, and a nice soundtrack that’s accessible through the phone’s music player.
It’s hard to categorize A Normal Lost Phone, but if you enjoy story-based games like Gone Home that progress quickly with very light puzzles, there’s a good chance you’ll enjoy this one, too. 3.5 stars, rated up because of the high quality art and music and the smooth interface.
